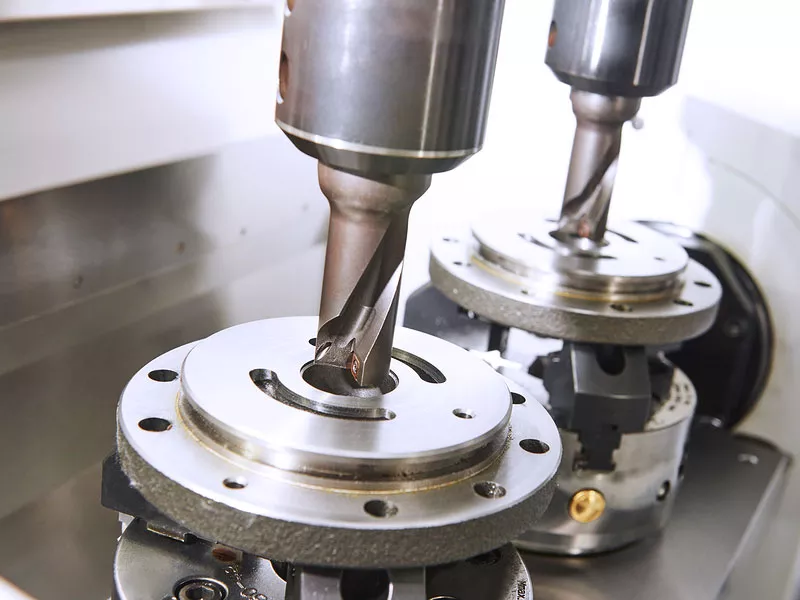
Several basic problems of CNC machining processing aircraft parts
The development trend of the modern aviation industry is high mobility, high safety, and new materials; therefore, a large number of integrated structures are used in aircraft, which greatly reduces the workload of aircraft assembly, improves the overall performance of the aircraft, and promotes the optimal development of aircraft structural performance. However, in the current manufacturing and processing industry, due to its processing process, materials, and other special characteristics, making the processing and manufacturing of deformation, the requirements for processing equipment are also relatively higher. For this reason, active and efficient process technologies should be adopted to improve the quality and efficiency of CNC machining of aircraft structural parts and to promote the development of the aviation industry. This paper clarifies some basic issues of CNC machining of aircraft structural parts to provide a reference.
What is aircraft parts machining?
Aircraft parts machining uses CNC machine tools to remove material from a workpiece using precise tools to create a final product. CNC machining is used to manufacture components throughout modern aircraft, from landing gear (components such as brackets and torque linkages) to engines (compressors and turbines). Structural components such as fuselage, bulkhead, and airframe components can also be CNC machined. Gears, shafts, and housings, which are important for moving parts, are often CNC machined parts. Finally, especially in helicopters, piston engine housings are often CNC machined.
What accuracy does a CNC machine have in machining aircraft parts?
Because aircraft parts often have complex geometries, the primary goal is to reduce weight and, at the same time, maximize strength or promote airflow over the surface of the part. Therefore sometimes, these complex geometries are unnecessarily complicated. For example, when internal components are designed to have complex organic surface geometries. Since higher complexity means more machining time and possibly more time to find capable suppliers, it is best to simplify part design and use extremely high-precision CNC machines to machine the corresponding parts whenever possible.
Because of the complexity and demanding nature of aircraft parts, the machining of aircraft components requires extremely high precision, often measured in thousandths of an inch. CNC machines for aircraft parts machining must maintain a high level of accuracy when machining various materials, including metals, composites, and plastics. In general, CNC machines used for aircraft parts machining should achieve an accuracy of at least +/- 0.0005 inches.
Why use 5-axis CNC for aircraft parts machining?
Five-axis CNC machine tool is a high technology, high precision machine tool specifically for processing complex surfaces; this machine tool system has a pivotal influence on a country’s aviation, aerospace, military, scientific research, precision instruments, high precision medical equipment, and other industries.
Five-axis CNC machining, in addition to the X, Y, and Z axis, there is a rotary axis and a swing axis. The rotation axis can be A axis or B or C axis; the rotation axis can rotate 360 degrees; the swing axis is in addition to the rotation axis that has been defined (such as A axis), the remaining two axes of one (such as B or C), swing axis can only swing within a certain angle (such as plus or minus 90 degrees) and can not rotate 360 degrees.
The five-axis machining center has high efficiency and precision characteristics, and the workpiece can be completed in one clamping of the five surfaces. It can process complex spatial surfaces with high precision and adapt to the processing of modern molds such as automotive and aircraft structural parts. The rotary axis of the vertical 5-axis machining center currently used by ANPLLO has two ways: the table rotary axis, the table set on the bed, can rotate around the X-axis, defined as the A-axis. The A-axis generally works from +30 degrees to -120 degrees. There is also a rotary table in the middle of the table that rotates around the Z-axis, defined as the C-axis, which is all 360 degrees of rotation. With the combination of A and C axes, the workpiece fixed on the table can be processed by the vertical spindle on all five sides except the bottom. The minimum indexing value of the A and C axes is generally 0.001 degrees, so the workpiece can be subdivided into arbitrary angles to produce inclined surfaces, inclined holes, etc. Complex space surfaces can be processed if the A and C axes are linked with the three linear axes XYZ.
Other machines generally cannot be designed with a large table and a small load-bearing capacity, especially when the A-axis rotation is greater than or equal to 90 degrees. The workpiece cutting will bring a large load-bearing moment to the table. The other is to rely on the rotation of the vertical spindle head. The front end of the spindle is a rotary head, which can surround the Z-axis 360 degrees by itself and become C-axis. There is an A-axis with rotation around the X-axis on the rotary head, which can generally reach ±90 degrees or more.
The above functions. The advantage of this setup is that the spindle processing is very flexible, and the table can be designed to be very large so that the huge fuselage of airliners and huge engine cases can be processed on this type of machining center.
Another advantage: when using spherical milling cutters on curved machine surfaces, when the centerline of the tool is perpendicular to the machining surface, the surface quality of the workpiece cut at the vertex will be poor because the vertex line speed of the spherical milling cutter is zero, and the design of the spindle rotation makes the spindle turn at an angle relative to the workpiece so that the spherical milling cutter avoids vertex cutting and ensures a certain line speed, which can improve the surface quality. Therefore, the five-axis machining center can meet the requirements of aircraft parts processing.
And aircraft parts often need complex shapes and angles. There the aircraft parts processing accuracy requirements and the type of material the traditional three-axis CNC machine tools can not achieve. Five-axis CNC machines can move the workpiece along five axes, creating more complex shapes and angles. This makes 5-axis CNC machining ideal for manufacturing aerospace components with complex geometries, such as turbine blades and engine components.
Why are complex aircraft components machined to the highest standards?
Aircraft components must meet strict safety standards and regulations to ensure the safety of passengers and crew. To meet these safety requirements, complex aircraft components must be machined to the highest standards. Even small deviations in size or surface finish can affect the performance of an aircraft component, potentially leading to catastrophic failure. Machining aircraft parts to the highest standards helps ensure that the final product meets all necessary safety requirements and performs as expected.
ANPLLO is a trusted supplier of aircraft parts machining
ANPLLO is a trusted supplier of aircraft parts machining, providing high-quality CNC machining services for a wide range of aerospace components. With years of experience in the aerospace industry, ANPLLO has the expertise and equipment necessary to create complex aircraft parts with the highest precision and accuracy. ANPLLO’s state-of-the-art CNC machines and expert personnel ensure that each part meets all necessary safety standards and performs as expected. Contact ANPLLO today to learn more about their aircraft parts machining services.