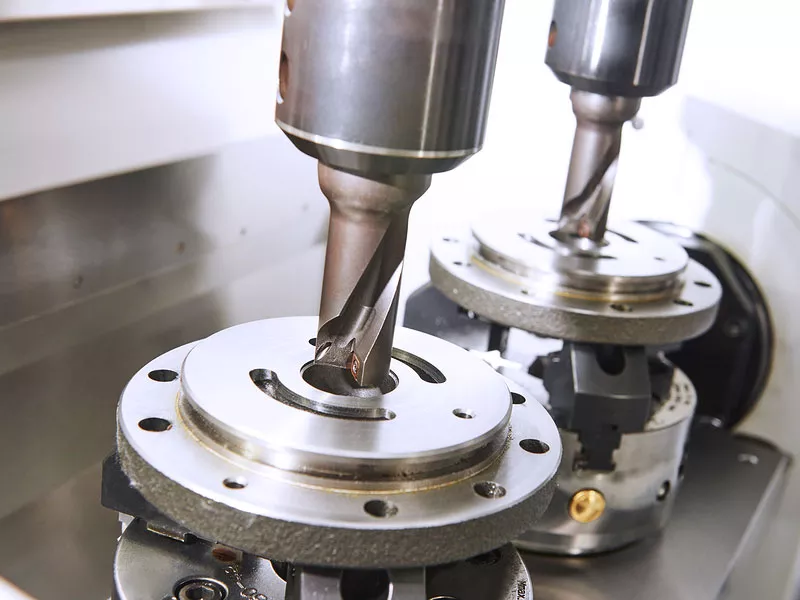
Processing Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene (ABS) Polymers
Table of Contents
Acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS) is a versatile thermoplastic known for its easy processing, coloring, and adaptability to additives. It is commonly used in toys, everyday items, and critical applications such as electrical insulators and automotive parts. Anpllo has many years of experience machining complex parts from thermoplastics such as ABS. This question provides Anpllo’s expertise on what goes into machining ABS and how it differs from other manufacturing methods.
Designers want to choose the right material for a project, and that requires a very good understanding of the data on the properties of the thermoplastic used for the part. Suppose you are working with ABS materials for your parts. In that case, it is important to know that ABS is a plastic engineering material with impact and chemical resistance, ideal electrical insulation and additional moisture resistance, good strength and stiffness, and excellent aesthetic qualities. It is also available in various glossy, plate-ready grades, making it a popular choice for processing parts that require high color and aesthetic appeal.
ABS is one of the most commonly used thermoplastic polymers in manufacturing today. It is inexpensive compared to other performance thermoplastics and offers good mechanical properties, including impact resistance, toughness, and rigidity. It is easily modified with additives to improve its properties, making it the polymer of choice for a wide range of applications.
ABS is typically classified as ABS for extrusion and ABS for injection molding, offering high and medium impact resistance. ABS generally has useful properties over a temperature range of -20 to 80°C (-4 to 176°F). It has no true melting point as an amorphous polymer because various additives can modify its properties.
Since its discovery, ABS has been used on a large scale in various consumer products, such as Lego blocks, tape recorders, golf club heads, household vacuum cleaners, and more. Nowadays, it also has large-scale end-use applications in industry, including automotive trims and components, medical devices, electrical components and assemblies, toys, housings/lids, and kitchen appliances.
At Anpllo, our close ties with the industry’s leading plastics manufacturers give us additional insight and access to technical assistance in material selection, sizing, and manufacturing procedures. Our machinists can help with material selection, sizing, and manufacturing techniques from concept to completion.
In our experience: To perform CNC machining of ABS materials, the critical machining process is mastering annealing and stress relief. And coolants, lubricants, and perfect machining procedures prevent cracks and cracking in parts that are being precision machined. In the annealing process of thermoplastics, slow heating and cooling reduce the heat generated and the chance of stress generation during the processing of polymers such as ABS. Our machinists use computer-controlled annealing furnaces to give precise temperature and time control for the highest quality machined parts.
To summarize, ABS is a versatile and popular thermoplastic that is easy to machine, modify and adapt to various applications. An experienced CNC machining company will do this by keeping data on the properties of the thermoplastic parts they produce, allowing their machinists to select the right material and machining method for the customer’s project, and ensuring that the final part produced is the one that meets the customer’s end-use requirements. At Anpllo, our machinists are experts in machining ABS and can provide insight and access to technical assistance in material selection, sizing, and manufacturing procedures.