Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) 3D Printing Service
Fused deposition modeling couples 3D printing’s unparalleled design freedom and fast lead times with production-grade thermoplastics to create durable parts with excellent mechanical properties. This technology is ideal for functional prototypes, durable manufacturing tools, and low-volume end-use parts, and is suitable for aerospace and other industries that rely on certified manufacturing. Anpllocnc provides rapid prototyping and low-volume on-demand production with FDM 3D printing service.Upload your CAD file to get instant quotes on FDM 3D printed parts.
Additive Parts for Your Toughest Needs with Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
The appeal of FDM 3D printing lies in its ability to quickly and accurately manufacture parts and prototypes for a variety of applications. From concept models to functional prototypes and even final use parts, FDM technology is adaptable and reliable. Its cost-effectiveness is another significant advantage.
Our industrial FDM machines serve industrial, aerospace and medical prototyping and production Our industrial FDM machines serve industries including industrial, aerospace and medical from prototyping to low-volume production at our certified FDM 3D printing facilities A global network will enable you to produce high-precision parts with quality and strength comparable to injection molding. Our expertise in additive manufacturing, high-end functional test prototypes, 24-hour service, competitive pricing, and on-time delivery with direct shipping to over 150 countries help you turn your ideas into projects and bring them to life faster. Bring your innovative products to the market, reduce your production costs and save your research and development time. Upload your CAD files, receive instant fused deposition modeling 3D printing quotes, and put your parts into production.
Get FDM 3D Printing Parts Now
Are you seeking an additive technology that can help you validate your part designs for fit, finish and functionality – and produce production parts? Do you wish that these parts could also withstand a variety of extreme environments?
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) is the iron man of additive technologies, able to help you with your rapid prototyping, part validation and low-volume production needs, using the same thermoplastic materials you use for injection molding.
Upload your CAD file to get instant quotes on FDM 3D printed parts.
General Tolerances for FDM 3D Printing
| Tolerance Note | Description |
|---|---|
General Tolerance | +/- a single build layer thickness for the first inch and +/- .002” for every inch thereafter. |
Build Size | Up to 24″ x 36″ x 36″ |
Layer Height, less than 16″ | 0.010″ Layers (0.008″ for PLA) |
Layer Height, greater than 16″ (up to 36″) | 0.013″ Layers |
Minimum Wall Thickness | 0.047″(less than 16″), 0.060″ (greater than 16″) |
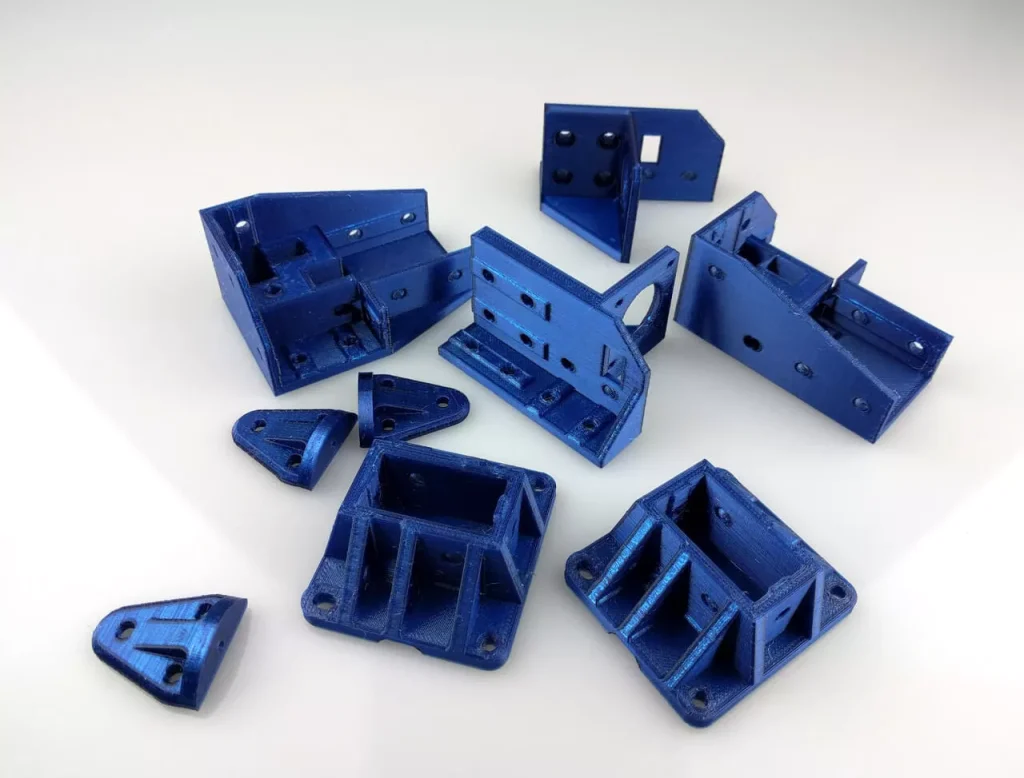

FDM 3D Printing Materials
TPU is a flexible, abrasion resistant material used for both consumer products and industrial use. They are extensively used in automobile manufacturing for parts like flexible tubes etc.
HIPS is very similar to ABS, in fact, it’s actually stronger. HIPS is easily painted, machineable, and works with a large number of adhesives. It’s also food-safe, non-toxic, fully recyclable, and non-hygroscopic, meaning it won’t degrade in humid environments.
Marble PLA is a PLA based flament that gives marble like finish to your models. This gives a rustic look and is perfect for sculpture like models. This is also bio-degradable. You get all the benefits of PLA and then some.
PLA is a bio-degradable material that is typically used for LEGO, electronic housings, medical devices and automobile parts. PLA has good strength properties suitable for prototyping various parts.
ABS is a very moldable material which makes it most suitable for a lot of applications ranging from toys to automobiles. It is widely used in 3D printing due to its light weight, moldability and low cost.
Wood PLA is wood fibers infused PLA material that gives a wood like finish to your models. This gives a twist to your routine models and gives them a unique look.
FDM 3D Printing Finishes
3D printed parts often tend to have layer marks .Some 3D printing processes use support materials too which can also leave marks to the surface of printed parts. These marks can be smoothed out using various grades of sand paper while maintaining the dimensional accuracy to a good extent.
Some materials like ABS react with acetone vapours. When they react with acetone it causes the surface of the part to smoothen with a glossy finish.
Post processed 3D prints can be painted to any choice of colour after priming and puttying rendering the finished parts an impeccable automotive grade finishes.
Traditional Technologies That Can Benefit from FDM
If you’re currently using CNC machining, injection molding or other traditional methods to produce prototype parts, FDM may be a faster and more flexible alternative.
FDM can be used to produce low-production runs of thermoplastic parts, ideal for bridge production or while you’re waiting for conventional manufacturing tooling to be completed.
What is FDM 3D printing technology?
FDM printers work by the addition of layers using FDM filaments. It is one of the most used additive manufacturing technologies, appearing as a natural alternative to traditional manufacturing processes.
During the FDM 3D printing process, the filament is extruded through a nozzle which melts while being gradually deposited in a structured way on the build platform until the object is finished. The extruder of the 3D printer is attached to a system with three axes: X, Y, and Z directions. When the material is melted and extruded, it is deposited in predetermined locations on the 3D printing bed, where it cools and solidifies. The bed lowers for each new layer, and this process repeats until the object is completed.
There is also particular importance of support structures in filament 3D printing technologies. While 3D printing with FDM technology, support structures are often required. Indeed, some geometries, such as overhangs, can’t be printed without supports.
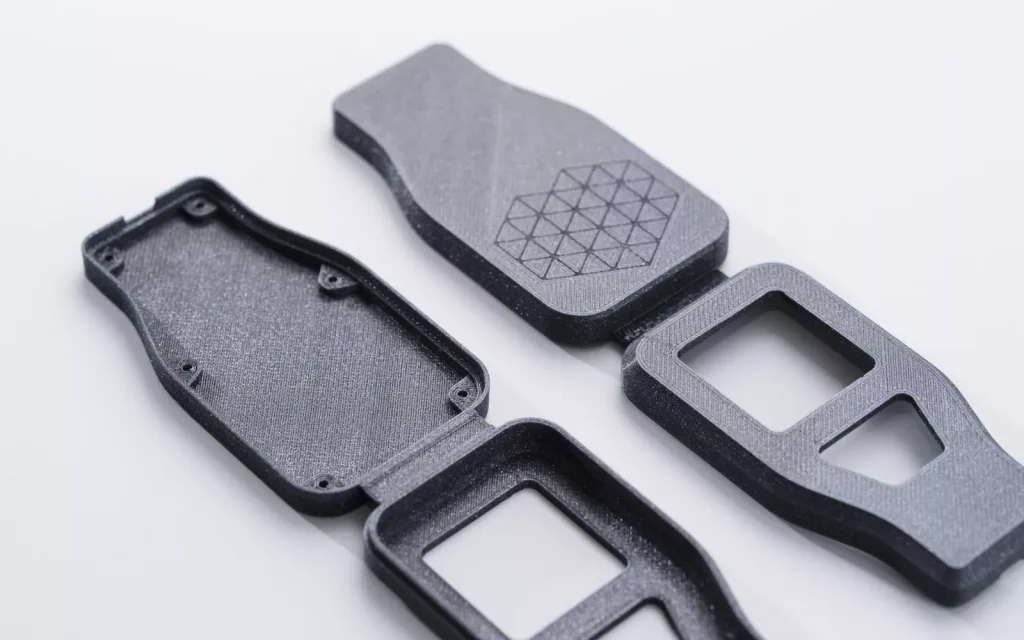

How Does FDM 3D Printing Work?
This is Steps of FDM 3D Printing Process :
- First, load a roll of thermoplastic filament into the printer. Once the nozzle reaches the desired temperature, the filament is fed into the extrusion head and melted in the nozzle.
- The extrusion head is connected to a 3-axis system so that it can move in the X, Y and Z directions. The melted material is extruded into thin strips and deposited layer by layer in predetermined locations, where it cools and solidifies. Sometimes the cooling of the material can be accelerated by using a cooling fan mounted on the extrusion head.
- To fill an area, multiple passes are required (similar to using markers to color a rectangle). Once a layer is complete, the build platform will move down (or in other machine setups, the extrusion head will move up) and deposit a new layer. Repeat this process until the part is complete.
Fourth, to support, post-processing work.
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) Process
Step 1
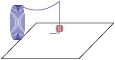
Energy is applied, material is extruded through heated nozzle.
Step 2
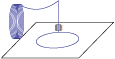
One layer/cross-section is applied to the build platform.
Step 3
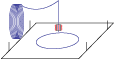
Platform is lowered and next layer of material is fused to the previous layer. Process is repeated.
Step 4

Completed part is then ready to remove from build plate.
Benefits Of Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
The advantages of industrial-grade FDM include durability, large printing volumes, material selection, high reliability, and high production efficiency.
- Durability: Industrial-grade FDM uses production-grade thermoplastic materials to produce durable, high-strength, and high-toughness parts suitable for high-load and high-durability applications.
- Large printing volume: Many industrial-grade FDM printers have large printing volumes, which can produce large or batch parts.
- Material selection: Industrial-grade FDM can use a variety of production-grade thermoplastic materials, such as ABS, PC, PPSU, ULTEM, to meet the requirements of various applications.
- High reliability: Industrial-grade FDM printers have high precision and stability and can produce consistent and reliable parts.
- High production efficiency: Industrial-grade FDM can achieve automated production, reduce labor and time costs, and improve production efficiency.
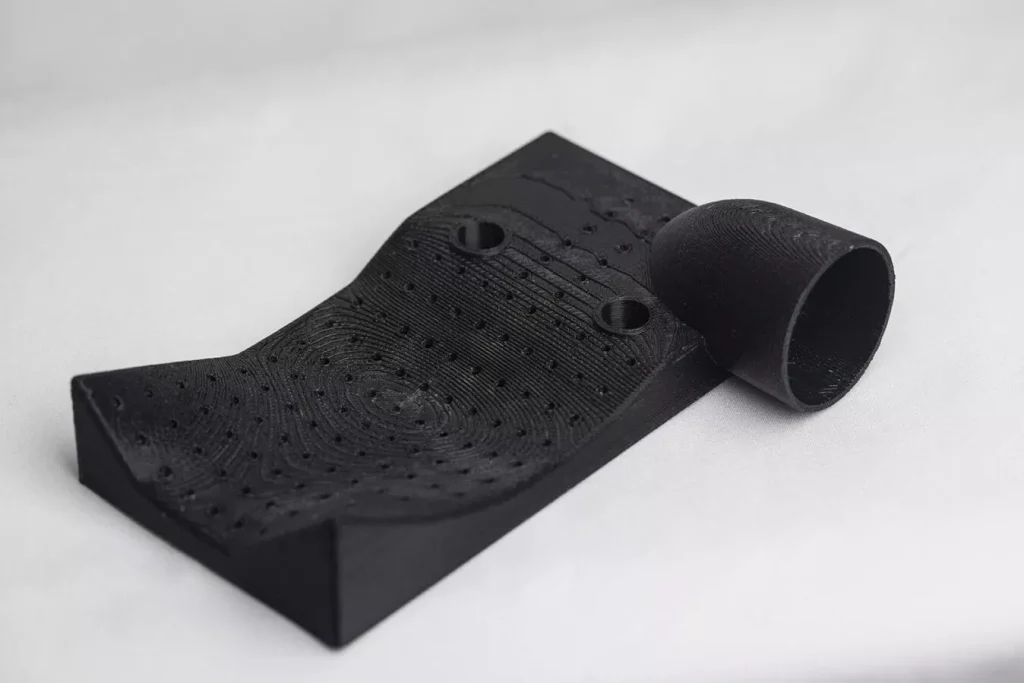

Applications of FDM
FDM parts are durable, chemical resistant and can endure extreme conditions, making them ideal for prototype testing and end-use parts. As FDM technology continues to advance, more and more industries are adopting this technology, including:
- Automotive
- Aerospace
- Architecture
- Medical and dental
- Pharmaceutical
- Health and beauty
FDM vs SLA
SLA printing is short for Stereo Lithography. Like FDM, it is an additive or layering method of 3-dimensional printing. Instead of filaments of material, SLA uses photopolymer resins that are liquefied and then cured with focused or UV light. While FDM printers support a range of materials, SLA printers are limited to proprietary materials that might not work with other SLA printer models. FDM offers more color choices too. Where SLA printing has the advantage is in precision accuracy and resolution/smoothness that produces crisper detail.
FDM vs SLS
SLS printing stands for selective laser sintering. The process uses a powerful laser to fuse plastic particles together into the desired 3D design. FDM has the advantage of being less costly and faster than the SLS process when producing single parts. SLS is more efficient for large-scale parts production. In addition, no support structures need to be printed with SLS as they do in some FDM designs.
FDM vs PolyJet
The PolyJet printing process employs a carriage equipped with ports that jet liquefied polymers to print the item. As in SLA, the polymers are cured with a UV light. FDM offers the production of larger part sizes, better heat resistance and greater part strength. PolyJet has the advantage of greater detail precision, smoother surface and more rapid printing.
contact us
Ready to get started on your 3D printing quote?
Our integrated approach to design, prototyping, and production allows you to bring your concept to market faster and more cost-effectively than virtually anyone else.
