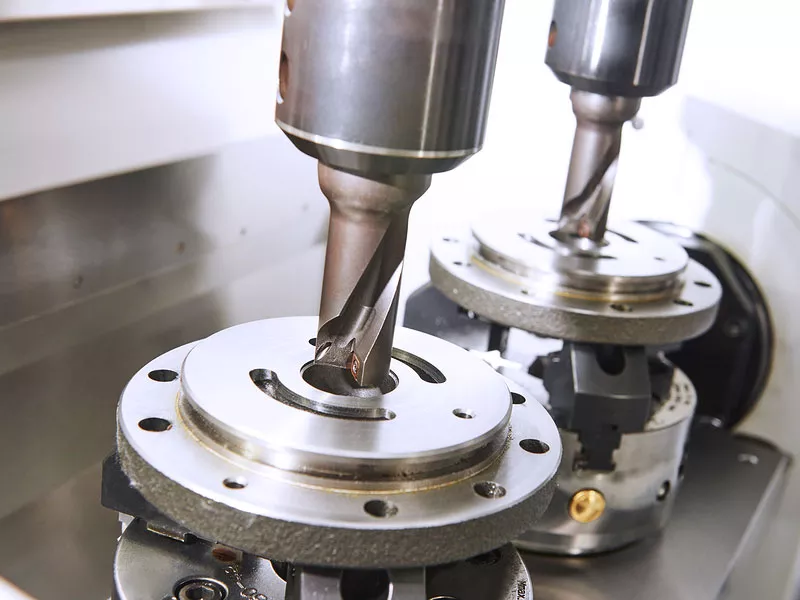
Customized processing methods and all processes for non-standard sheet metal parts
Table of Contents
Sheet metal can be processed to produce many devices. Non-standard custom sheet metal can be designed according to the customer’s required drawings. Many different manufacturing processes are used, and the process depends on the starting metal material and the product required by the customer. Both custom products and stock products are handled. Most custom metal fabrication products are made from various common metals and their alloys. Using the sheet metal process to polish the raw material, we can also provide after-sales services such as deburring, polishing, painting and painting the product. Sheet metal is used for automotive parts and heavy machinery. When manufacturing sheet metal, manufacturers often use the following forming processes. Stamping is a common sheet metal forming process. A punch and die are used to punch holes in the sheet metal.
In addition, when arranging the process, non-standard sheet metal custom fabricators often have to consider whether bending is good or not and whether they can bend because bending is a very important process. Bending is a good operation that directly affects the quality assurance of bending. The products produced by non-standard sheet metal custom fabricators are increasingly widely used. The design of sheet metal parts has become very important in product development. After mechanical engineers master the design skills of sheet metal parts, they can make the designed sheet metal products meet the functional requirements.
The whole process of non-standard custom sheet metal parts
The full process of non-standard custom sheet metal parts usually includes the following.
Design: The first step is to design the custom sheet metal part. This involves creating a 2D or 3D design of the part using computer-aided design (CAD) software. The customer usually provides this step. However, the non-standard sheet metal fabricator’s engineers must consider the material type, thickness and any necessary bending or cutting when reviewing the customer’s design. To provide suggestions for improvements to the customer.
Material Selection: Once the design is complete, the next step is to select the right material for the part. Common sheet metal materials include steel, aluminium, copper and brass: The choice of material will depend on the requirements of the part, such as strength, corrosion resistance and weight.
Cutting: The sheet metal is cut to the desired size and shape using various techniques such as laser cutting, plasma cutting or waterjet cutting. The cutting process must be precise to ensure that the part meets design specifications and that companies avoid high scrap rates.
Forming: The sheet metal is then shaped into the desired shape using various techniques such as bending, rolling or stamping. Forming is done using specialized machines and tools that apply pressure to the metal to form the desired shape.
Finishing: Once a sheet metal part is formed, it may require finishing to improve its appearance and function. Finishing techniques may include polishing, painting, powder coating, anodizing, or plating. The surface finishes offered by manufacturers who can take non-standard custom sheet metal parts are generally more complete. Therefore, when processing non-standard custom parts, you can reduce the cost of communication back and forth and the cost of time and money.
Assembly: If the sheet metal part is part of a larger product, it may need to be assembled with other components. Assembly can be accomplished using various techniques such as welding, fastening or adhesives.
Quality Control: Finally, the sheet metal parts are inspected to ensure they meet the design specifications and necessary quality standards. Quality control may include measuring dimensions, checking surface finish, and performing functional tests.
Customizing a sheet metal part involves a combination of design, material selection, cutting, forming, finishing, assembly and quality control. The exact steps will depend on the specific requirements of the part and the manufacturing process used. Only by serving our customers with care and attention the development of our business will not be a problem.
What are the industry categories of non-standard custom sheet metal fabrication?
About what industry category does non-standard custom sheet metal processing belong? What sheet metal belongs to that industry? We know sheet metal processing is the repair of automobile shells, a classification of automobile repair. However, sheet metal processing application industries are mainly manufacturing, but almost all industries are involved. Sheet metal processing products mainly include automatic equipment shells, engineering lines, kiln plates, and precision mechanical parts. For different electronic equipment, different thickness standards are used. The mounting plates inside distribution cabinets and cabinets are generally not less than 2.5mm, and the standard for outdoor cabinets is not less than 1.5mm. The main raw materials for the sheet metal processing industry are non-ferrous alloy plates and thin steel. The non-ferrous metal and steel industries account for about 40% of the total industrial cost. Sheet metal processing only accounts for 20% ~ 30%. Still, a large part of the manufacturing industry involves sheet metal processing, such as computer, agricultural machinery, fitness, textile, electrical instrumentation, health, kitchen and bathroom, office, etc. There are several other issues to be noted in sheet metal processing. First, the staff should check the material before processing and expand the material for processing purposes. The material should be developed in the right way so that the material can be saved during processing and the purpose of processing can also be achieved. The choice of gap and material edge effect should also be noted during processing.
Customized processing methods for non-standard sheet metal parts?
Currently, bending and stretching are mainly carried out for sheet metal parts. The order of bending processing is mainly from inside to outside, from small to large, folding special cases first and then folding general shape priority processing. Non-mould processing and mould processing. Although their processing processes are more or less the same, they always escape the following points: The design department designs pictures according to the requirements of the sheet metal processing parts and presents them one by one in the form of 3D to facilitate the processing department and fully display the sheet metal parts? The use of sheet metal processing can be made into various styles, specifications and functions of finished products. The steel frame structure goods produced have strong strength, rigidity, and better load-bearing capacity.
In the production process of non-standard sheet metal parts, each part of the structure can be integrated and assembled into structural parts by welding, riveting and stamping by certain positions, specifications and precision, so the customization is flexible. To sum up, sheet metal processing has the following characteristics. The materials commonly used in sheet metal processing are cold rolled sheet (SPCC), hot rolled sheet (SHCC), galvanized sheet (SECC, SGCC), copper (CU) brass, copper, beryllium copper, aluminium sheet (6061, 6063, hard aluminium, etc.). Depending on the role of the product, different materials are used, and the available product needs to be considered in terms of its usage and cost. Several reasons exist for the elastic deformation of parts in sheet metal processing. One is that if the internal structure of certain parts contains thin sheets, there will be higher requirements on the operation method. Otherwise, the operator cannot correspond to the drawing design when positioning and clamping the parts, which will easily lead to the generation of elastic deformation.