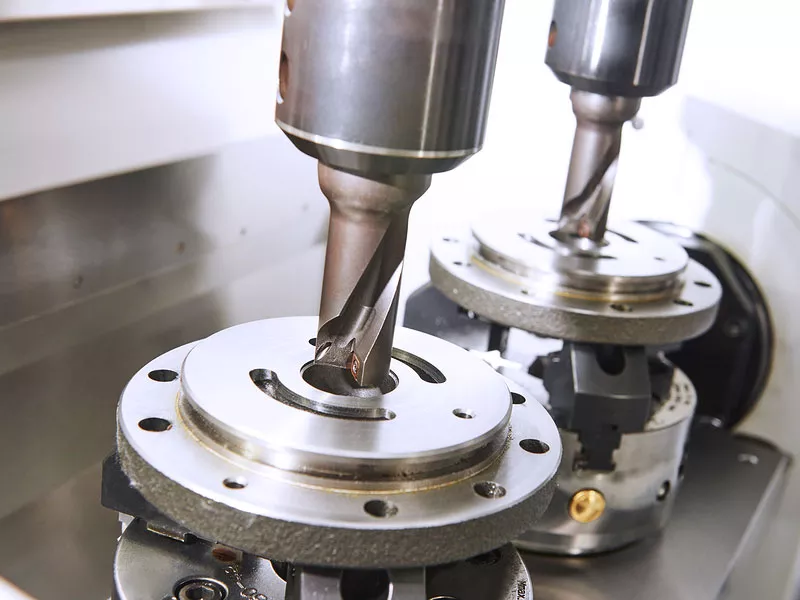
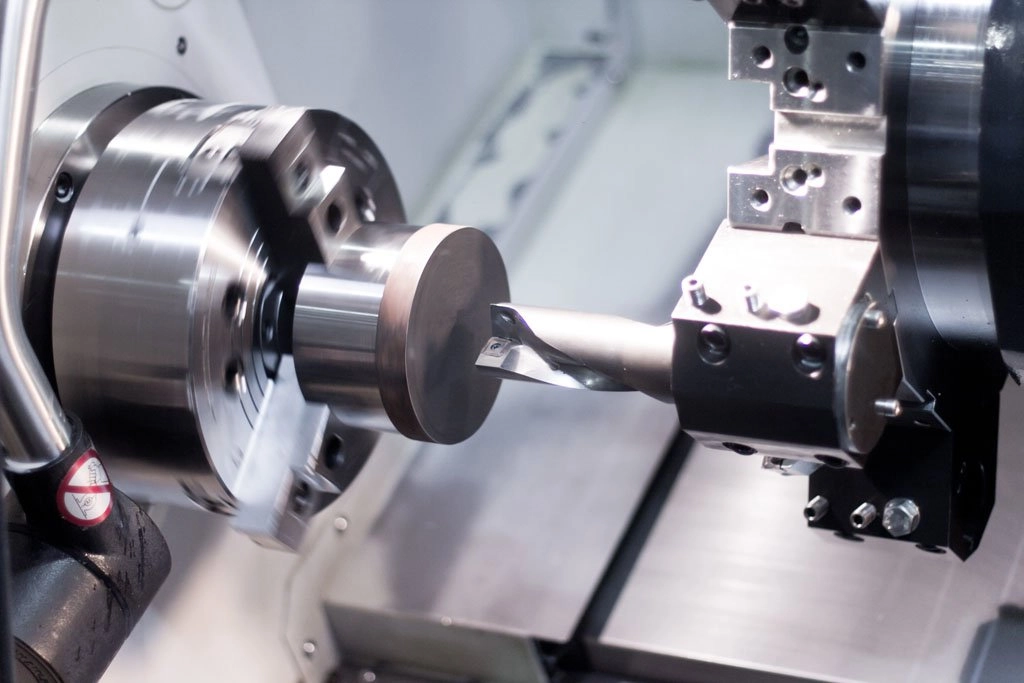
Characteristics and applications of CNC ultra-precision machining technology
- Characteristics and applications of CNC ultra-precision machining technology
Introduction: CNC Precision and ultra-precision machining technology is an important way to improve the performance, quality, working life, and reliability of electromechanical products, as well as to save materials and energy.
For example: improving the machining accuracy of cylinders and pistons can improve the efficiency and horsepower of automobile engines and reduce fuel consumption; improving the machining accuracy of the rolling body and raceways of rolling bearings can improve the speed of bearings and reduce vibration and noise; improve the flatness of disk machining, thus reducing the gap between it and the magnetic head, can greatly improve the storage capacity of disks; improve the precision of the inscription of semiconductor devices (reduce line width, increase density) can improve the integration of microelectronic chips.
What are the CNC precision machining technologies?
The structure of the cutting tool and the relative motion form of the cutting tool and the workpiece determines the process characteristics of CNC precision machining. According to the process characteristics, cnc processing can generally be divided into turning, milling, drilling, boring, reaming, planing, inserting, broaching, sawing, grinding, lapping, honing, super-finishing, polishing, gear processing, worm wheel processing, thread processing, ultra-precision machining, clamping, and scraping.
According to the removal rate and precision, points can be divided into.
①Rough machining: with a large depth of cut, by a time or a few times to go away from the workpiece to cut most or all of the machining allowance, such as rough turning, rough planing, rough milling, drilling, and sawing, Etc., rough machining processing efficiency and processing accuracy is low, generally used as a pre-processing, sometimes can also be used for final processing.
② semi-finishing: generally used as an intermediate process between roughing and finishing, but the workpiece precision and surface roughness requirements are not high parts and can also be used as the final processing.
③Finishing: fine cutting is used to make the machined surface reach high precision and surface quality, such as fine-tuning, fine planing, reaming, fine grinding, Etc. Finishing is generally the final processing.
④Finishing machining: After finishing machining, the purpose is to obtain smaller surface roughness and slightly improve the accuracy. Finishing machining has a small allowance, such as honing, grinding, super-finishing grinding and super-finishing machining, Etc.
⑤ Finishing processing: the purpose is to reduce the surface roughness to improve corrosion resistance, dustproof performance, and improve appearance, and does not require improved precision, such as polishing, sanding, Etc.
⑥Ultra-precision machining: aerospace, laser, electronics, nuclear energy, and other cutting-edge technology requires some special precision parts, an accuracy of up to IT4 or more, and a surface roughness of no greater than Ra 0.01 microns. This requires special measures for ultra-precision machinings, such as mirror turning, mirror grinding, soft abrasive mechanical chemical polishing, Etc.
Distinguished by the surface formation method
In cutting, the machined surface of the workpiece is obtained by the relative motion of the cutting tool and the workpiece.
Cutting processing can be divided into 3 categories according to the surface formation method.
① Tool tip trajectory method: rely on the tool tip trajectory relative to the workpiece surface to obtain the required surface geometry of the workpiece, such as turning the outer circle, planing plane, grinding the outer circle, turning forming surface with a die, Etc. The tooltip’s trajectory depends on the motion of the cutting tool and the workpiece provided by the machine tool.
② Forming tool method: the forming method, with the final surface profile of the workpiece matching the forming tool or forming wheel, Etc., processing the forming surface. At this point, part of the forming motion of the machine tool is replaced by the cutting edge’s geometry, such as turning, forming milling, and forming grinding. Due to the manufacturing difficulties of forming tools, machine tools – fixtures – workpieces – tools formed by the processing system can withstand the limited cutting force; forming method is generally used only for processing short forming surfaces.
③ spreading method: also known as a rolling cutting method, processing cutting tools and workpiece for relative spreading movement, the tool (or grinding wheel) and the workpiece of the instantaneous line of pure rolling each other, between the two to maintain a definite speed ratio relationship, the processing surface is obtained in this movement of the cutting edge envelope surface. Gear processing in hobbing, inserting, shaving, honing, and grinding (not including forming grinding).
Grinding is one of the main methods of precision machining of CNC parts, Generally used for radius machining and finishing. Grinding is one of the main methods for finishing precision and ultra-precision parts Grinding is one of the main methods for finishing precision and ultra-precision parts. The grinding process enables the parts to obtain high dimensional, geometric shape, and positional accuracy. The precision machining method is a machining method with a machining accuracy of 1 micron. Precision machining mainly includes fine-turning, boring, milling, grinding, and lapping processes. It is performed under strictly controlled environmental conditions.
Features of CNC precision and ultra-precision machining
Micro-scale machining refers to micro-nano machining, mainly using CNC precision and ultra-precision machining technology, micro-fine machining technology, and nano-machining technology to process, emphasizing the “very thin cutting” and microstructure, the size of the processing features are relatively small, in the micron, sub-micron, and nanometer level, the focus of research is the microstructure of the material; in between Between the two is called medium-scale machining or medium-size machining.
CNC precision machining can be divided into macroscale, mesoscale, and microscale machining according to the scale of workpiece processing features. Most of the usual machining refers to macro-scale machining; the technical performance requirements of the parts are reflected in the macro-scale or surface structure, the size of the processing features is relatively large, and the scope of processing is wider.
CNC precision machining and ultra-precision machining characteristics
The difference between CNC rough machining and finishing machining: rough machining removes more material, small cutting speed, large feed and draft, low dimensional accuracy, and low surface quality; finishing machining removes less material, large cutting speed, small feed, and draft, ensuring final dimensional accuracy and surface quality.
1、Rough machining is to quickly remove the balance of the blank for the purpose, in rough machining should be selected with a large feed and as large as possible depth of cut to remove as many chips as possible in a shorter period.
2, the fine particle-size oil stone is mounted on the vibration head of the finishing surface for finishing processing (see cutting processing). Superfinishing is generally arranged after the finishing grinding process. Its machining allowance is only a few microns, suitable for processing crankshafts, rolls, bearing rings, and various precision parts such as outer, inner, flat, groove surfaces, and spherical surfaces.
The development status and application of precision forming processing
The development status and application of the precision molding process, precision casting forming, precision molding, plastic processing, and thin plate precision forming technology in industrially developed countries are highly valued, and they invest much money to develop priority. In the 70s, the U.S. Air Force hosted the development of a “forging process modernization plan” with the purpose is to making forging this important process achieve. In 1992, the U.S. Department of Defense put forward a “military critical technology list,” which includes the isobaric forming process, CNC computer-controlled spinning, plastic transformation, shear forming machinery, superplastic forming/diffusion connection, hydraulic extension Forming process, and other precision plastic forming process. In recent years, foreign countries have also developed aerospace products for the application of “large die forging and blade forging process,” “rapid solidification powder lamination process,” “large complex structural parts of the powerful spin forming process, “superplastic forming process for difficult deformation materials,” “advanced materials (such as metal matrix composites, ceramic matrix composites, Etc.) forming process”, Etc. Superplastic forming technology is also applied in the aerospace and machinery industries, such as satellite components, missiles, and rocket cylinders in the aerospace industry, Etc. The superplastic forming method is used to manufacture the Chin alloy recovery capsule for reconnaissance satellites. At the same time, it also mastered the zinc, copper, aluminum, and Chin alloy super plastic forming process, the minimum forming thickness up to 0.3mm, and the shape is more complex. In addition, foreign countries have been widely used in manufacturing weapons precision molding technology. Commonly used precision molding technology, such as occlusion forging, precision forming, and isothermal forming using the principle of diversion, has been used in military production abroad. At present, precision molding technology in the application is still relatively small; the accuracy is also poor, with foreign accuracy of ± 0.05-0.10mm.
Anpllo CNC precision manufacturing
We are a senior manufacturer focusing on CNC precision machining; with many years of experience in the machining industry, the company has an advanced CNC machining center, five-axis machining center, four-axis machining center, three-axis machining center, machining accuracy of ± 0.005mm. The company also has a high-precision CNC turning center and professional testing equipment (five-axis three coordinates, that can achieve precision machining of various parts. CNC machining. Support a variety of titanium, titanium alloy, aluminum, stainless steel and copper, and other materials processing, the company has a complete pre-sales and after-sales service system, providing customers with one-stop processing services to ensure the quality and quantity of the pursuit of products! Welcome to customize with pictures and samples!


